The NASA News Line
April 11, 2002
Greetings!
News from out of this world:
————————————
Hot off the presses: Chandra X-ray Observatory has studied two separate supernova remnants, or neutron stars, and found evidence that they may, in fact, be composed of a new form of matter. The neutrons within them may be partly, or entirely, broken down into quarks. This finding, if confirmed, would be of fundamental importance in physics, and demonstrates the value of using space as a physics laboratory. https://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/2002/0211/index.html
Other CXO news: Chandra Finds Well-Established Black Holes In Distant Quasars – surprisingly, they look much the same as younger quasars, suggesting that they formed early and haven’t changed much. https://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/2002/highzqso/index.html
Still more CXO news: like snowballs in a blast furnace, Chandra has identified relatively cool lumps of gas around two large galaxies, within a much hotter cloud of gas that surrounds them. So why don’t they melt? https://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/2002/0150/index.html
————————————
Astronomers using RXTE have shown that the “tempo” of x-ray variations from a black hole is related to its mass. The smaller the black hole, the slower its “beat”. This could help pin down the masses of distant black holes.
Story at https://www.cnn.com/2002/TECH/space/04/09/black.holes/index.html
RXTE at https://heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/xte/xte_1st.html
————————————
Radar Pushes Limits of Asteroid Impact Prediction – we’re getting better at this, and there’s no reason to sell the farm. Story, with links to images and animations, at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2002/release_2002_79.html
————————————
NASA Spacecraft Finds Comet Has Hot, Dry Surface – a little surprising, for an icy body. Results from when our Deep Space 1 spacecraft flew by comet Borrelly in September, at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2002/release_2002_80.html
————————————
Primitive bacteria exist in huge numbers deep in the Earth, living on hydrogen gas produced in rocks. Sounds kinda dreary, but they don’t mind. https://amesnews.arc.nasa.gov/releases/2002/02_37AR.html
————————————
Some mission status updates:
After three weeks of in-orbit checkout, the Hubble Space Telescope has been declared healthy. However, the calibration process for the instruments will continue for another two months. The first Early Release Observations taken with the Advanced Camera for Surveys will be available in maybe 3-4 weeks. https://www.gsfc.nasa.gov/news-release/releases/2002/02-051.htm
Voyager Maintenance from 7 Billion Miles Away (that’s about 10,000,000,000 clicks for you metric types) – setting a record for long-distance repairs at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/solar_system/features/voyager.html
Our Cassini spacecraft successfully completed a course adjustment April 3 during its journey toward Saturn. It’s been 4.5 years since launch, and only about 2 to go. https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2002/release_2002_78.html
————————————
Cheers!
April 11, 2002
Relics of an ancient eruption that tore through a cluster of galaxies were recently uncovered by our Chandra X-ray Observatory. The discovery implies that galaxy clusters are the sites of enormously energetic and recurring explosions. https://chandra.harvard.edu/press/02_releases/press_010802.html
————————————
Like a hyperactive child, the Universe had an energetic youth, according to a new result using data from the Two-Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS). Evidence of early star formation at https://www.gsfc.nasa.gov/news-release/releases/2002/02-003.htm P.S. this afternoon we are hosting a press conference here at HQ to discuss related results from Hubble, about rates of starbirth in the VERY early Universe. You will probably be able to find that story online after 2pm EST at https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr.html
————————————
Scientists using RXTE see a few glitches in an otherwise flawless spin of a pulsar, revealing the strange physics of the high-pressure interior of the pulsar. A hiccuping neutron star at https://www.gsfc.nasa.gov/news-release/releases/2002/02-006.htm
————————————
NASA scientists using the Chandra X-ray Observatory have measured the distribution of dark matter in an elliptical galaxy and found that this mysterious substance exists in high concentrations throughout most of galaxy. The finding narrows the field of candidate theories that can explain dark matter. https://www.gsfc.nasa.gov/news-release/releases/2002/02-002.htm.
————————————
We have terminated the Full-sky Astrometric Mapping Explorer mission due to projected cost increases uncovered during mission studies. A shame, because it would have been cool science. The FAME page is still up athttps://www.usno.navy.mil/FAME/
if you want to check it out.
————————————
Flight controllers of our 2001 Mars Odyssey mission report that the aerobraking phase is proceeding right on schedule and should be completed soon, followed by the start of “normal” science operations. https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2001/release_2001_247.html
————————————
Do you like Junkyard Wars? NASA and its corporate partners will support robotics education for about 200 high schools in 2002 by sponsoring teams that will participate in a national robotics competition. We here in the Office of Space Science coordinate NASA’s involvement in this program. ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/2001/01-255.txt
————————————
Finally, HESSI launch is still slated for January 24. https://hesperia.gsfc.nasa.gov/hessi/
Cheers!
Nov 16, 2001
Just a few items of note in Space Science this week:
Along with the European Space Agency, we are performing tests of the communications system between our Cassini Saturn orbiter and the ESA Huygens Titan probe. The two craft will need to talk clearly to each other when they arrive at Saturn in July 2004. Story at https://spaceflightnow.com/news/n0111/16huygens/
————————————
The brightening and dimming of the sun may account for a 1,500-year cycle of cooling and warming on parts of the Earth. We’re living in the Sun’s atmosphere at https://www.cnn.com/2001/TECH/space/11/16/solar.cycles.ap/index.html
————————————
Our Genesis spacecraft will fire its engine today to enter its primary science orbit around the L1 Lagrangian point between earth and the Sun, where it will start to capture particles of the solar wind to bring back to Earth. Story at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2001/release_2001_222.html Actually, the engine firing should have occurred about 30 minutes ago; you should be able to find out soon at https://genesismission.jpl.nasa.gov/
————————————
NASA is doing several things related to this weekend’s Leonid meteor shower. There’s a press release about it at ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/2001/01-222.txt , but don’t just read about the Leonids – go out and watch them if you can. Watching comet dust vaporize is fun and entertaining!
————————————
Finally, just a note that we have another launch coming up: our TIMED mission to study the upper reaches of Earth’s atmosphere is scheduled for liftoff on December 7. Read up on TIMED and follow progress at https://www.timed.jhuapl.edu/
Cheers!
Nov 14, 2001
Greetings, universe fans,
Lots of news in Space Science:
Sky survey lowers estimate of asteroid impact risk – Sloan data suggests that there’s only a 1-in-5000 chance of an asteroid wiping out civilization in the next century. Previous estimates were about 1-in-1500. The sky is not yet falling athttps://www.sdss.org/news/releases/20011108.asteroid.html
————————————
Mars news:
Volcanoes Still Active on Mars? New Evidence for Ongoing Volcanism and Water Release – science bubbling athttps://www.geosociety.org/pubntrst/pr/01-54.htm
Discovery of Buried Impact Craters on Mars Widens Possibility of an Ancient Martian Ocean – an intoxicated scientist at https://www.geosociety.org/pubntrst/pr/01-56.htm
Finally, here at NASA HQ, we have selected 10 scientific investigations for the 2005 Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) mission. Part of our future Mars program gets defined at ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/2001/01-220.txt
————————————
The most powerful explosions in the universe, gamma-ray bursts, may come with a 10-second warning: an equally violent burst of ultra-high-energy particles called neutrinos. But detecting them won’t be easy. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2001/11/011106084012.htm
More GRB news: the afterglow of a gamma ray burst, first detected by our HETE-2 satellite, has been seen in x-ray, optical, and radio wavelengths. Story at ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/2001/01-218.txt ; HETE-2 at https://space.mit.edu/HETE/————————————
Using data from SOHO, scientists now have the first clear picture of what lies beneath sunspots, and have peered inside the Sun to see swirling flows of electrified gas or plasma that create a self-reinforcing cycle, which holds a sunspot together. This solves a major puzzle about the Sun, not that there aren’t plenty more remaining. Story at https://science.nasa.gov/headlines/y2001/ast07nov_1.htm?list52322 , SOHO at https://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/
————————————
First Estimate of the Formation Temperature of Ammonia Ice in a Comet – suggesting at the comet was formed between the orbits of Saturn and Uranus in the primordial Solar System nebula. A potential new tool for studying comets athttps://www.subaru.naoj.org/Science/press_release/2001/11/index.html
————————————
NASA’s 2002 Budget appropriation has been passed by both houses of Congress, and is headed to the President for signature. I’ve posted the Space Science excerpts athttps://spacescience.nasa.gov/announce/2002approp.htm
————————————
Reminder – the Leonid meteor shower this weekend could be a fantastic display. Rates of over 1000 meteors per hour have been predicted. Definitely worth climbing out of bed! Details at https://science.nasa.gov/headlines/y2001/ast08nov_1.htm
————————————
Cheers!
A few items:
New pictures of the south polar cap on Mars, and a global view of the dust storm occurring there, have been released by the imaging team for our Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft. https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2001/release_2001_188.html
————————————
While Hubble continues to show off the wonders of the cosmos, its 2.4-meter (94.5-inch) diameter back-up mirror goes on permanent display, starting tomorrow, as part of the “Explore The Universe” exhibit in the Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum here in Washington. ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/2001/01-185.txt
————————————
Also tomorrow: our Deep Space 1 spacecraft will be swinging by Comet Borrelly for its final act. Will it make it? https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2001/release_2001_187.html
————————————
Data from the Digitized Sky Survey has played an important supporting role in helping radio and X-ray astronomers discover an ancient black hole speeding through the Sun’s galactic neighborhood. An interesting piece of detective work at https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/2001/29/
————————————
Like a frozen turkey that just won’t thaw, a strange star near the center of the Milky Way is surprising astronomers with its remarkably low temperature. More Chandra results at https://chandra.harvard.edu/press/01_releases/press_090601freeze.html
————————————
Finally, thanks to my many readers, including many from overseas, who sent kind and thoughtful notes following last week’s attack on America. I also received many requests for an online address for Dr. Sagan’s remarks. The quote (and image of a distant Earth) can be found at https://www.seds.org/billa/psc/pbd.html , and a very nice printable poster version (1.8MB .pdf file) is available at https://www.seds.org/billa/psc/pbd.html . It looks great if you have a good printer and lots of ink. I’d also like to correct an error I made a couple of “issues” ago: I said that the Earth’s oceans reflect light better than the land. In fact, the opposite is true. The error was completely mine; the original story, about the possibility of using brightness variations to characterize extrasolar planets, is at https://www.spaceref.com/news/viewpr.html?pid=5874 .
————————————
Best wishes.
Science@NASA is based in the United States, but among many of its subscribers are a substantial number of readers from other countries. In recent days many of them have written to expressing their sympathies and horror at the events of Sept. 11th. Their messages, attached below, reveal how the heart-breaking loss of life in New York, Washington, D.C., and Pennsylvania touches everyone. The staff of Science@NASA extend its heartfelt condolences to the many victims of Tuesday’s tragedy, and thank its friends overseas for their kind messages of support as it resumes, later today, a regular schedule of scientific story-telling.
————————————
TO: Ron.koczor@msfc.nasa.gov
FROM: inna_mar@XXXXXXXX.ru
Dear Mr. Koczor, All of us are shocked by the awful events that have occurred yesterday in New York and in Washington and we wish to extend our sympathy to you and your colleagues. If there is any way that we can help, please let us know. Sincerely, Inna Mardanyan Moscow, Russia
************************************
TO: Ron.koczor@msfc.nasa.gov
FROM: gushat@XXXXXXX.ru
Dear friends, Your colleagues from Paleontological Institute of Moscow are with you.Our sympathy, thoughts and support are yours. And will always be.Best regards, Alexei Rzanov, Galina Ushatinskaya, and all colleagues from Moscow
************************************
TO: Ron.koczor@msfc.nasa.gov
FROM: snassopoulou@XXXXXXX.gr
Dear Ron, We are very sorry and really left astonished and speechless with terrorism struck US yesterday. We sincerely wish and hope that everything is OK for you and all the American colleagues and families.
Yours, Sophia
Athens, Greece
************************************
TO: phillips@spacescience.com
FROM: tony.taggett@XXXXXXX.uk
Dear Dr Phillips As my only point of contact with the United States is through your science@NASA website, I would like to express my heartfelt condolences to the American people, our thoughts and prayers especially go out to the relatives and friends of those who perished in the awful events that occurred yesterday
Yours Sincerely
Tony Aggett
United Kingdom
************************************
TO: ron.koczor@msfc.nasa.gov
FROM: mmazzolini@XXXXXX.au
We would like to offer our deepfelt sympathy, concern and prayers to our friends and colleagues in the US at this dreadful time, Margaret and Alex Mazzolini Melbourne, Australia
************************************
TO: ron.koczor@msfc.nasa.gov
FROM: omaro@XXXXXX.kz
We are absolutely shocked by horrible events in the U.S. It is unbelievable…Accept my condolences…Today our world has changed. What will happen to our world?
Take care,
Prof Omarov
Alma Aty, Khazakstan
************************************
TO: ron.koczor@msfc.nasa.gov
FROM: cofXXXXX@home.com
As the President of CANADIAN Environmental Science and Research Group and on behalf of the Team of CESAR Group I would like to send our heart felt sorrow to those family members who lost relatives in these vicious and despicable attacks on democracy. God Bless America!
Jack Pender
Canada
************************************
From: Rafael Cárdenas Santacruz
To: Ronald.J.Koczor@msfc.nasa.gov
Sincere greetings Dr. Koczor, Ron Together with my family, we feel very sorry for the regrettable incidents in New York. We are with you with all our hearts. Rafael Cardenas SantacruzScientific Technician
Bogota, Columbia
************************************
TO: Ron.koczor@msfc.nasa.gov
FROM: jarl.ahlbeck@XXXXX.fi
In the 1930’s Stalin deported and murdered 25,000 Finns that were peacefully living on the Soviet side of the border. It was a blind terror action against civilians, a complete ethnical cleaning of the Karelia county. Without successful defensive fight in the following winter war 1939 when Stalin tried to invade Finland (5 of my uncles were killed, my father injured), we would, according to recently discovered documents from Moscow, all have been deported to Siberia, and I would not sit here and study your website. These terrorists try to create a world of that kind. We do not want this world anymore!
All the best for you in the USA Jarl
Helsinki, Finland
************************************
Necochea, 11/9/01
TO: ron.koczor@msfc.nasa.gov NASA:
Hi¡, My name is Maria. I am aware of the attack that has been perpetrated against your country, and I am very sad. I live in Buenos Aires, Argentina. I am 14 years old and there is not much that I can do to help, but I profoundly admire you and you have my moral support. I would like to ask you a favor. Please reach an agreement without wars, but I hope those responsible are found, so that peace will be extended throughout the world.
Sincerely, Maguie.
************************************
From: Jonathon Dugdale
To: patrick.meyer@msfc.nasa.gov
Sent: 9/11/01 12:37 PM
Subject: Condolences On behalf of all the employees and stakeholders of ApexMail I would like to say that we share in your shock, grief and pain resulting from today’s unspeakable and cowardly assault. Our thoughts and prayers are with you and the people of America.
Jonathon Dugdale
Apexmail, Inc Canada
The following is by courtesy of Craig Tupper and Space Science at NASA,and is a weekly service
Greetings, universe fans.
A few recent items of interest at https://spacescience.nasa.gov :
————————————
The “giant impact” theory, first proposed in the mid-1970s to explain how the Moon formed, has received a major boost as new results demonstrate for the first time that a single impact could yield the current Earth-Moon system. And did you know that Earth’s day used to be only 5 hours long? https://www.swri.org/9what/releases/canupmoon.htm
————————————
Well Preserved Meteorite Yields Clues to Carbon Evolution in Space – a fresh meteorite, unlike other similar space rocks, contains very few amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. Implications for the origins of life at https://www.asu.edu/asunews/Releases/Meteor0801.htm
————————————
Because the Earth’s oceans reflect light better than the land, it would appear to “flicker” in brightness to a far distant observer. This fact might provide an additional technique for eventually locating an Earth-like planet around another star. Story at https://www.spaceref.com/news/viewpr.html?pid=5874 , and check out Terrestrial Planet Finder (a big goal for our future) at https://tpf.jpl.nasa.gov/
————————————
Violent gas collisions that produced supersonic shock fronts in a dying star are seen in a new, detailed image from our Hubble Space Telescope. The future of the Sun in 5 billion years at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2001/release_2001_179.html
————————————
A spiky landscape of bright ice and dark dust shows signs of slow but active erosion on the surface of Jupiter’s moon Callisto in new images from our Galileo spacecraft. The pictures give the highest resolution view ever seen of any of Jupiter’s moons. So what causes the erosion? Story at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2001/release_2001_178.html , Galileo at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/
————————————
A spiky landscape of bright ice and dark dust shows signs of slow but active erosion on the surface of Jupiter’s moon Callisto in new images from our Galileo spacecraft. The pictures give the highest resolution view ever seen of any of Jupiter’s moons. So what causes the erosion? Story at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2001/release_2001_178.html , Galileo at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/
————————————
We have selected seven new recipients for grants to institutions to help implement our education and outreach program. And the winners are…:/ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/2001/01-175.txt
————————————
Cheers!
Greetings!
Thanks to my many readers who noticed that spacescience.nasa.gov had not been updated for a while. It’s nice to know someone’s watching! I’ve been on vacation, now I’m back and here’s the latest and coolest:
————————————
A team of astronomers has found a Jupiter-sized planet orbiting a faint nearby star similar to our Sun. There are now two large known planets in this system, in orbits comparable to that of Jupiter, raising intriguing prospects of finding a solar system like our own. Press release at ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/2001/01-166.txt , images at https://www.nsf.gov/od/lpa/news/press/01/newplanet.htm
————————————
There’s a very cool (but large, 3mb or more) animated movie or our CONTOUR mission, scheduled for launch next summer to visit some comet nuclei. Worth it! https://www.contour2002.org/news3.html
————————————
A nearby young star recently gave birth to millions of comets, and now it is destroying them, according to new observations using our Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer spacecraft. Fickle. https://www.gsfc.nasa.gov/news-release/releases/2001/01-81.htm
————————————
Astronomers using our Chandra X-ray Observatory have taken a look at the plane of the Milky Way galaxy and found that its X-ray glow comes from hot and diffuse gas. The findings help to settle a long-standing mystery about the source of the X-ray emission from the galactic plane. https://chandra.harvard.edu/press/01_releases/press_080901.html
————————————
NASA scientists recently proposed a new explanation for the rise of oxygen in Earth’s early atmosphere – an event that may have jumpstarted the evolution of complex life. https://www.spaceref.com/news/viewpr.html?pid=5687
————————————
New Hubble Space Telescope snapshots reveal dramatic activities within the core of the galaxy NGC 3079, where a lumpy bubble of hot gas is rising from a cauldron of glowing matter. Pretty cosmic violence at https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/2001/28/
————————————
Our Galileo spacecraft is transmitting scientific information from its most recent dash past Jupiter’s moon Io. Details at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2001/release_2001_172.html
————————————
A prototype of an airplane that someday may fly over Mars has successfully completed a high-altitude flight test. https://amesnews.arc.nasa.gov/releases/2001/01_58AR.html
————————————
Scientists have successfully tested a key instrument for GLAST, our next-generation gamma-ray telescope that will eventually stare down the barrel of massive black hole particle jets. Story at https://www.gsfc.nasa.gov/news-release/releases/2001/01-78.htm , GLAST at https://www-glast.sonoma.edu/
————————————
Cheers!
Greetings!
A few new things posted in the past week at https://spacescience.nasa.gov/ :
Space Science News for February 10, 2000
Kamikaze Comets: Ninety-two sungrazing comets discovered by the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory appear to have come from the breakup of a single gigantic comet more than 2000 years ago. SOHO’s 100th – 102nd comet discoveries came just this week. FULL STORY at https://spacescience.com/headlines/y2000/ast10feb_1.htm
NEWS NOTE: Launch of the Japanese/U.S. Astro-E spacecraft occurred last night, but the spacecraft has been lost. The Japanese project website carries this statement:
“After 6 years of hard work by a dedicated staff of scientists, engineers, and administrators, Astro-E was launched on February 10, 2000 at 1030 JST, from Kagoshima Space Center… Unfortunately, there was a problem with the first stage of the M V rocket. Astro-E could not obtain the necessary altitude for a proper orbit. As a result, the satellite was declared unusable.”
This mission was described in a recent SpaceScience.com science news story,
“Colder than Space.”
https://spacescience.com/headlines/y2000/ast07feb_1.htm
For more information about the launch see
https://www.astro.isas.ac.jp/xray/mission/astroe/astroeE.html
You are subscribed to the SpaceScience.com mail server. This is a free service. Follow the instructions at the bottom of this message if you wish to unsubscribe. Thanks! –Tony Phillips, Editor
You are currently subscribed to sciencenews as: ehcurrie@worldnet.att.net To unsubscribe send a blank email to mailto:leave-sciencenews-29028N@spacescience.sparklist.com
————————————
Our Stardust spacecraft has successfully completed a three-part deep space maneuver designed to keep it on target for an Earth gravity assist in January 2001. After whipping by the home planet, Stardust will head for a meeting with comet Wild-2 in January 2004.
status report: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/status/std/sd20000126.html
Stardust home: https://stardust.jpl.nasa.gov/
————————————
Mission managers have decided to send another set of commands to Mars to investigate the possibility that a signal detected by a radio dish at California’s Stanford University came from Mars Polar Lander. There’s no real hope that any science can be salvaged, but it would be interesting to know that the spacecraft landed successfully. https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/marsnews/mpl/status/mpl20000125.html
————————————
Hubble Space Telescope is back in business, as made dramatically evident in stunning new celestial pictures of remote galaxies and a colorful dying star released Monday. I often stay away from superlatives, but I just gotta leave that “stunning” in there for these images, especially that “dying star”.
galaxies: https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/2000/08/index.html
dying star (Eskimo nebula): https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/2000/07/index.html
————————————
Several new images from Chandra were released last week, including:
Chandra Images Seething Cauldron of Starburst Galaxy (M82) – https://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/cycle1/0094/index.html
Chandra Finds “Cool” Black Hole at the Heart of Andromeda (M31) –https://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/cycle1/0007/index.html
Chandra Discovers X-ray Source at the Center of Our Galaxy (looks like a black hole) – https://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/cycle1/0204/index.html
Chandra Finds Oxygen Ring in Ashes of Exploded Star – https://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/cycle1/0015/index.html
Chandra Finds X-ray Star Bonanza in Orion Nebula – https://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/cycle1/0054/index.html
————————————
We have decided to delay the High Energy Transient Explorer (HETE-2) launch to the mid-May time frame, in order to perform additional testing. Once we get it up there, HETE-2 will go about its business of detecting and localizing gamma-ray bursts (enormously energetic cosmic explosions). Learn more athttps://space.mit.edu/HETE/
Space Science News 1/18/2000
Greetings!
As expected, a ton of results were released at last week’s American Astronomical Society meeting. Of course, not all of them involved data our spacecraft… but many of them did, and there was a lot of exciting stuff! Here’s some of the best, plus a few more things that aren’t AAS related:
————————————
In what has been hailed as a major discovery, our Chandra X-ray Observatory has resolved most of the X-ray background, a pervasive glow of X-rays throughout the Universe, which was first discovered in the early days of space exploration. Before now, scientists have not been able to discern the origin of the hard, or high-energy, X-ray background, because until Chandra no telescope has had the technology to resolve it. At the same time, Chandra may have revealed the most distant objects ever seen in the Universe, and discovered two puzzling new types of cosmic objects.https://chandra.harvard.edu/press/00_releases/press_011400bg.html
————————————
The planetary dust disk around the star Beta Pictoris is dynamically “ringing like a bell,” according to astronomers investigating NASA Hubble Space Telescope images. They think that the disk may have been “rung” by the passing of a nearby star around 100,000 years ago.https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/2000/02/
————————————
A team of astronomers conducting a systematic search for supermassive black holes has discovered three more of the mysterious objects lurking in the centers of nearby elliptical galaxies, and suggest that black holes formed early and influenced galactic evolution.https://www.umich.edu/~newsinfo/Releases/2000/Jan00/r011000c.html
————————————
Astronomers using a new technique to measure cosmic distances (based on Hipparcos data) are finding that the universe may be expanding faster than previously thought. https://cfa-www.harvard.edu/cfa/ep/kstanek0100.html
————————————
Astronomers using data from COBE and 2MASS have announced the discovery of a new cosmic signal that should lead to a better understanding about the creation of stars in the early universe.https://www.uclanews.ucla.edu/Docs/SWHL005.html
————————————
A primordial soup of complex organic chemicals that could be the precursors of life is cooked up very quickly after the birth of stars, new research based on ISO data suggests.https://dailynews.yahoo.com/h/ap/20000112/sc/life_out_there_1.html
————————————
Peering deep into a distant galaxy, astronomers have obtained a glimpse of what may be the youngest massive star clusters ever observed. https://www.news.wisc.edu/thisweek/view.msql?id=3538
————————————
Astronomers using Hubble have found that the ages of three globular clusters in a nearby galaxy are very different, with one of the clusters being only about 100 million years old. The findings have implications for theories of galaxy evolution. https://www.washington.edu/newsroom/news/2000archive/ 01-00archive/k011200.htm
————————————
Two international teams of astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based telescopes in Australia and Chile have discovered the first examples of isolated stellar-mass black holes adrift among the stars in our galaxy. https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/2000/03/index.html
————————————
Astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope imaged the Bubble Nebula, an expanding shell of gas from a dying star, with unprecedented clarity. For the first time, they are able to understand the geometry and dynamics of this very complicated system. More info and beautiful pics at https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/2000/04/
————————————
NASA scientists taking a census of large asteroids in our solar system neighborhood have cut their estimate in half. https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2000/neat.html
————————————
We currently have two large scientific balloons flying simultaneously over Antarctica. One is studying the Sun, the other is looking at Earth’s aurora. You can keep track of the flights through the NSBF web site by going to https://192.149.107.80/default.html and clicking on “Operations,” then “Antarctica Operations,” then whichever flight track you wish to view first. Fun!
————————————
The extended halo of half-million-degree gas that surrounds the Milky Way was generated by thousands of exploding stars, or supernovae, as our galaxy evolved, according to new observations by our Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) spacecraft. ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/2000/00-005.txt More FUSE results announced at the AAS are available at the FUSE page, https://fuse.pha.jhu.edu/
————————————
A sequence of colorful images detailing a stellar explosion in another galaxy show a supernova’s massive, morphing shock wave, providing scientists with a case study in the structure and evolution of the events. Story at https://explorezone.com/archives/00_01/07_supernova_evolution.htm
————————————
The Mars Polar Lander flight team has ended all attempts to regain communications with the spacecraft. JPL press release at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2000/mplend.html
————————————
Astronomers from around the world will gather in Japan later this month to present the most detailed images of quasars ever seen, produced with data from the Very Long Base Interferometry Space Observatory Program. JPL press release at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/2000/spacevlbi.html
————————————
Finally, don’t miss the total lunar eclipse this Thursday night, January 20. A good page for details is at https://sunearth.gsfc.nasa.gov/eclipse/SEextra/TLE2000Jan20.html
>Cheers!
December 14, 1999
Hello universe fans,
Here’s what’s new in Space Science at https://spacescience.nasa.gov/ :
————————————
Still no word from Mars Polar Lander or Deep Space 2. Attempts will be made to spot MPL using the Mars Global Surveyor; if anything can be seen, it might help us understand what went wrong. There’s a story on this at https://www.space.com/science/solarsystem/mpl_search_991213.html ; the latest JPL mission status report is at https://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msp98/news/mpl991210.html In better Mars news, a team of astronomers using data from Mars Global Surveyor has found evidence consistent with ancient oceans on Mars. story: https://www.brown.edu/Administration/News_Bureau/1999-00/99-060.html images: https://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/mgs/sci/mola/dec10-99rel/ocean_paper.html MGS page: https://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/mgs/
————————————
From May 10-12, 1999, the solar wind that blows constantly from the Sun virtually disappeared — the most drastic and longest-lasting decrease ever observed. Remember to check the weather before you go out into space! Story and images at https://www-istp.gsfc.nasa.gov/istp/news/9912/immovies.html
————————————
The European Space Agency’s X-ray Multi-Mirror spacecraft was launched successfully on December 10, and seems to be doing well so far. We are playing a role in this mssion, which in many ways complements our Chandra X-ray Observatory. ESA XMM page: https://sci.esa.int/missions/xmm/ GSFC press release describing our involvement: ftp://pao.gsfc.nasa.gov/pub/PAO/Releases/1999/99-137.htm Meanwhile, a Chandra image of the Hydra A galaxy cluster has revealed a possible solution to a puzzle about the fate of such huge clusters. Press release at ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/1999/99-142.txt , image at https://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/0087/
————————————
Frozen bugs! Scientists have discovered a microbial world hidden deep beneath the frozen Antarctic ice that could help them learn more about how life can survive under extreme conditions on other planets or moons. What about in the fridge? https://george.arc.nasa.gov/dx/basket/pressrelease/99_81AR.html
————————————
Hubble Servicing Mission 3A launch on shuttle mission STS-103 was reset (again) for December 16, and seems to be on track. https://hubble.gsfc.nasa.gov/
————————————
For years astronomers have been looking for the cause of the 1843 explosion of the stellar system Eta Carinae, and to explain the strange hourglass shape. A team of astronomers using ESA’s infrared space telescope, ISO, have now succeeded, putting the blame firmly on a previously undetected very massive ‘donut’ of dust. https://sci.esa.int/missions/newsitem.cfm?TypeID=18&ContentID=8091
Cheers!
————————————
Subscribe: send blank e-mail to oss-update-subscribe@onelist.com
Unsubscribe: send blank e-mail to oss-update-unsubscribe@onelist.com Archives: https://www.onelist.com/archive/oss-update Space Science home: https://spacescience.nasa.gov/SPACE SCIENCE NEWS DECEMBER 7, 1999:
There are a lot of disappointed folks around here. Most of you probably know from news reports that we have failed to hear from either the Mars Polar Lander or the Deep Space 2 microprobes after their arrival at Mars on December 3. Following another failed attempt last night, mission controllers for Mars Polar Lander acknowledge that they hold out very little hope of communicating with the spacecraft. The Deep Space 2 microprobes have also been silent, and are probably lost as well. The latest JPL status report is at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/marsnews/mpl/status/mpl991207.html . Assuming the worst, my condolences go to the project teams and to everyone involved, who worked hard to attempt what will always be a technological feat – landing on another planet.
Of course, we hate failure around here, not only for the loss of science but also for the loss of U.S. taxpayer money. Rest assured that we will be scrutinizing our entire program from top to bottom, including the way we have implemented the “Faster-Better-Cheaper” philosophy. However, it is worth pointing out that despite several failures in the past year, small/cheap Space Science spacecraft have had about the same failure rate as larger missions — around 10%, excluding rocket failures. That doesn’t mean that there is no room for improvement, but the conclusion that F-B-C has inherently led to more failures is poorly supported by the evidence. Space is a risky business, and the trade-offs between risk, cost, and other factors will continue to be debated. But we cannot go back to the days when spacecraft routinely cost $1 billion each.
In other, mostly better news:
————————————
Massive clouds of gas, discovered long ago but only recently identified as being within the margins of the Milky Way, play a key role in the ability of the galaxy to churn out new stars by raining gas onto the plane of the galaxy. Story and images at https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/1999/46/index.html
————————————
Galileo has completed the closest-ever encounter with Jupiter’s volcanic moon Io, but not before giving ground controllers a Thanksgiving day white-knuckler. Once again, the Galileo team came through brilliantly. Story at https://galileo.jpl.nasa.gov/news/status/status991125.html
————————————
A team of astronomers has found six new planets orbiting nearby stars. This brings the total number of known planets outside the solar system to 28, all of which have been found within the last five years. HQ press release at ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/1999/99-140.txt
————————————
Hubble Servicing Mission 3A launch on shuttle mission STS-103 was recently reset for December 11, and now looks like it will slip another day or two due to additional minor shuttle fixes. Follow the action at https://hubble.gsfc.nasa.gov/ and https://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/status/stsstat/current.htm
————————————
Links to the Mars Network project, currently under study as a possible future element within our Mars Surveyor program, have been added to our Missions pages.
Mars Network: https://marsnet.jpl.nasa.gov/
Missions pages: https://spacescience.nasa.gov/missions/index.htm
————————————
Here’s a bit of legal-ese that you may be interested in:
Pursuant to the National Environmental Policy Act of 1969 (NEPA), as amended (42 U.S.C. 4321 et seq.), the Council on Environmental quality Regulations for Implementing the Procedural Provisions of NEPA (50 CFR Parts 1500-1508), and NASA policy and procedures (14 CFR Subpart 1216.3), NASA has prepared and issued a Draft Environmental Impact Statement (DEIS) for the Mars Surveyor 2001 Mission. The DEIS addresses the potential environmental impacts associated with continuing the preparations for and implementing the Mars Surveyor 2001 (MS 01) mission. Interested parties are invited to submit comments or environmental concerns on or before January 17, 2000, or 45 days from the date of publication in the Federal Register of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s notice of availability of the MS 01 mission DEIS, whichever is later.
The DEIS is at https://spacescience.nasa.gov/pubs/Mars01EIS/ms01webpage.html
————————————
A rock-hunting robot that we are supporting is being sent to Antarctica on a mission that will likely turn up the first meteorites discovered by a machine rather than a human. MSNBC story at https://www.msnbc.com/news/340170.asp , project page at https://www.bigsignal.net/
Best wishes.
What’s new at https://spacescience.nasa.gov/ :
11/10/99
————————————
The first report from the Mars Climate Orbiter failure investigation board was released today. Many of you already know that the primary cause was a ailure to convert English units to metric. The report identifies a number of other “process” problems that allowed this error to go undetected. A lot of folks are sweating to make sure this doesn’t happen again.press release: ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/1999/99-134.txt Board report: ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/reports/1999 /MCO_report.pdf (that’s 355kb in Adobe Acrobat format; get the reader free at https://www.adobe.com/products/acrobat/readstep.html)
PBS television in the U.S. will be airing Life Beyond Earth, a two-hour special that tells the story of humanity’s search for extraterrestrial life, tonight and this weekend. Looks like a great show, featuring Dr. Timothy Ferris, author of The Whole Shebang (and several other excellent books). Schedule and a few more details at (you’ll have to cut and paste this enormous URL-sorry!) https://www.pbs.org/plweb-cgi/fastweb?getdoc+whatson+whatson+ 7335+0+wAAA+%28whatson%3AAREA%29%26AND%26%28 Life%29%26AND%26%28science%3Awosubjects%29%26AND %26%28199911%3Awomonth%29 or just check your local listings.
————————————
Evidence shows lots of galaxies made the background glow – results from the Infrared Space Observatory, with implications for the early history of the universe. Story at https://explorezone.com/archives/99_11/10_esa_galaxies.htm ISO page at https://isowww.estec.esa.nl/
————————————
A test flight was successfully conducted recently of a pumpkin-shaped balloon half the size of a football field, and approximately one-tenth the volume of our planned Ultra Long Duration Balloon (ULDB). The ULDB will stay aloft at altitudes of up to 115,000 feet (35 kilometers) for as long as 100 days with more than a ton of scientific instruments. For some experiments, this could be cheaper than going to space, and just as effective. This is a capability we have wanted for a long time; now it may be just around the corner. press release: ftp://pao.gsfc.nasa.gov/pub/PAO/Releases/1999/ W99-112.htm
balloon page: https://www.wff.nasa.gov/pages/scientificballoons.html
————————————
Hubble Servicing Mission 3A has been delayed a few days due to a decision to change out one of shuttle Discovery’s engines. The new target date is December 6. https://hubble.gsfc.nasa.gov/
————————————
Last week we gave the go-ahead to ASPERA-3, the first Mission of Opportunity to be selected as part of our Discovery Program. The ASPERA (Analyzer of Space Plasmas and Energetic Atoms) experiment is one of seven scientific instruments that will fly on the European Space Agency’s Mars Express mission, planned to launch in mid-2003. The main objective of the mission is to search for sub-surface water from orbit and drop a lander on the Martian surface. ASPERA-3 doesn’t have a web page yet; when it does I will link to it at https://spacescience.nasa.gov/missions/index.htm . Meanwhile, you can check out the ESA Mars Express page at https://sci.esa.int/missions/marsexpress/ , or our Discovery program page at https://discovery.nasa.gov/index.html
————————————
Astronomers using radio telescopes have gained their first glimpse of the region near a black hole at the heart of a distant galaxy, where a powerful stream of subatomic particles spewing outward at nearly the speed of light is formed into a beam, or jet. These are the most detailed images ever of the center of the galaxy M87, some 50 million light-years away. https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/1999/43/
Meanwhile, our Chandra X-ray Observatory has made an extraordinary image of Centaurus A, a nearby galaxy noted for its explosive activity. This image shows an x-ray jet from another black hole in unprecedented detail. https://science.nasa.gov/newhome/headlines/ast26oct99_1.htm
————————————
Ancient iron-rich rocks point to early occurrence of land-based life on Earth — implications for astrobiology at https://www.eurekalert.org/releases/psun-air101899.html
————————————
Hubble has allowed astronomers to resolve, for the first time, hot blue stars deep inside an elliptical galaxy. Hubble confirms that the ultraviolet light comes from a population of extremely hot helium-burning stars at a late stage in their life. https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/1999/40/
————————————
The latest images from Mars Global Surveyor suggest the presence of “pseudocraters”, formed by explosions due to the interaction of molten lava with a water-rich surface, a long time ago. So where did Mars’ water go? https://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/mgs/msss/camera/images/ 10_22_99_gsa_cones/index.htm
————————————
The popular image of young planetary systems as thin, spinning pancakes of cosmic dust and debris may be changed by a new computer model that shows how a disk of debris is transformed into a very distinct ring once Pluto-like bodies start to form. https://www-cfa.harvard.edu/cfa/ep/kenyon1099.html
————————————
The closest-ever image of Jupiter’s moon Io, taken during a flyby of the volcanic moon by our Galileo spacecraft, shows a lava field near the center of an erupting volcano. https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/99/glliohighres.html
Cheers!
Craig
23 October 1999
————————————
Not too long ago a story came out with evidence from Hubble that some giant stars had swallowed up giant planets. That story is at https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/1999/24/index.html . Now there are new observations suggesting that many smaller, sun-like stars may also have swallowed giant planets. Or maybe not. Story at https://www.newscientist.com/ns/19991023/newsstory12.html
————————————
The Florida Today newspaper has posted an excellent section on life elsewhere in the universe, covering many of the issues and the status of current research. https://www.flatoday.com/space/explore/special/contact/index.htm
————————————
Hubble examines the Rotten Egg Nebula, a pretty picture and a good story with implications for the understanding of dying stars, at https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/1999/39/
————————————
The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) has recorded a series of 3 rapid-fire coronal mass ejections on the Sun. The sun has been a bit less active than predicted lately, but it is still gearing up for “solar maximum”, perhaps in the middle of next year. SOHO page: https://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/ Nice story at https://science.nasa.gov/newhome/headlines/ast15oct99_1.htm
————————————
More solar news: Bright Rings Found around Sunspots Show Why Spots Are Dark, Cast Shadow on Solar Models-we still have a lot to learn about the most important star in our sky. National Science Foundation press release at https://www.nsf.gov/od/lpa/news/press/99/pr9963.htm .
Cheers!
October 12, 1999
What’s new at https://spacescience.nasa.gov/ :
————————————
Two complementary surveys by independent teams of astronomers using Hubble show that the hubs of some galaxies formed early in the Universe, while others formed more slowly, across a long stretch of time. Press release at ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/1999/99-107.txt
Now, for lots of interesting tidbits about our neck of the cosmic woods, the solar system:
————————————
Two teams of researchers have proposed the existence of an unseen planet or a failed star circling the sun, far beyond the orbit of Pluto. The idea is based on a study of the orbits of long period comets, visitors from the Oort cloud. Fascinating story at https://www.msnbc.com/news/320182.asp?cp1=1
————————————
An international team of astronomers using a ground-based telescope has discovered a moon orbiting the asteroid (45)Eugenia. The pictures are the first of an asteroidal satellite taken from Earth, and the second ever taken; the Galileo spacecraft previously discovered a moon around the asteroid Ida.
Story at https://www.eurekalert.org/releases/nsf-asa100699.html
Ida image at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/mess34/Moon1.html
And in current Galileo news, it seems that sulfuric acid — a corrosive chemical found on Earth in car batteries — exists on the frozen surface of Jupiter’s icy moon Europa. Are there any implications for the possibility of life there? There’s a press release at ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/1999/99-112.txt , and an image is available at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/
————————————
Neptune and Uranus contain a high proportion of methane, which researchers have now shown can turn into diamond at the high temperatures and pressures found inside these planets. Don’t ask your local jeweler for one of these, yet. https://www.urel.berkeley.edu/urel_1/CampusNews/PressReleases/ releases/9-30-1999a.html
————————————
Scientists studying high-resolution images from our Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft have concluded there is no evidence of shorelines that would have surrounded oceans that may have once existed on Mars. Images and discussion at https://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/mgs/msss/camera/images/grl_99_shorelines /index.html
Press release: ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/1999/99-114.txt————————————
Cheers!
September 17, 1999
Latest Space Science News.
Greetings,
What’s new at https://spacescience.nasa.gov/ :
————————————
Curved cracks on Europa present additional strong evidence for a subsurface ocean, according to a new study based on Voyager and Galileo data. Let’s go fishin’. story at https://www.spaceviews.com/1999/09/16c.html
nifty animations at https://pirlwww.lpl.arizona.edu/~hoppa/science.html
Galileo: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/
Voyager: https://vraptor.jpl.nasa.gov/voyager/voyager.html
————————————
Hubble Spies Giant Star Clusters Near Galactic Center – peering through the dust, HST sees violent starbirth activity. https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/1999/30/
————————————
Our Mars Climate Orbiter (MCO) spacecraft fired its maneuvering engines yesterday morning for 15 seconds, to adjust its flight path for arrival at Mars next week. Meanwhile, the first image of Mars from MCO has been released. It doesn’t look like much, but that’s what you get from 4.5 million kilometers away. It does show that the camera is working.
Engine firing story: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/status/mco/mco990915.html
MCO page with first image: https://mpfwww.jpl.nasa.gov/msp98/orbiter/
————————————
Evidence supporting one of two competing ideas about the rate and timing of star formation in the universe has been released. The new study suggests that most stars formed very early in the history of the universe. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/1999/09/990915080958.htm
————————————
Massive black holes may be the force behind half of the universe’s radiation produced after the Big Bang, chipping away the coveted power monopoly believed to be held by ordinary stars. ftp://pao.gsfc.nasa.gov/pub/PAO/Releases/1999/99-098.htm
————————————
The first image from Chandra’s High Resolution Camera has been released, showing a 3000 year old supernova remnant. While Chandra continues to perform well, the team is addressing a concern with part of the Advanced Charge-coupled Device Imaging Spectrometer (ACIS) science instrument.
HRC image: https://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/0050/index.html
ACIS concern: https://www1.msfc.nasa.gov/NEWSROOM/news/ status/chandrastatus/chandrastatus49.html
————————————
Although inspections and repairs of electrical wiring are continuing, Space Shuttle managers last week announced tentative target launch dates for the next two Shuttle missions. Managers established the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission 3A as the next Shuttle flight, and had targeted launch for no earlier than Oct. 28, 1999. But that was before Hurricane Floyd shut down the Kennedy Space Center the last couple days. A new launch date should be announced soon. You can follow the mission at https://spaceflight.nasa.gov/shuttle/
————————————
Cheers!
September 8, 1999
Hello space science fans,.
What’s new at https://spacescience.nasa.gov:
————————————
A new study of images from Mars Pathfinder (has it really been two years?) has revealed a number of dust devils. Story and short “movie” at https://explorezone.com/archives/99_09/08_dust_devils.htm
————————————
The discovery of a new type of low-surface-brightness reflection nebula around aging stars has provided important clues about how stars lose mass and form planetary nebulae. Live 5 billion years and watch the sun do it! https://www.eurekalert.org/releases/uiu-ntp090799.html
————————————
Recent observations have confirmed that magnetic fields are a critical component controlling when and how stars form. https://www.eurekalert.org/releases/uiuc-mfg090799.html
————————————
A troupe of four galaxies imaged by HST is performing an intricate dance, orchestrated by the mutual gravitational forces acting between them. A pretty picture at https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/1999/31/index.html
————————————
Uranus’ 20th moon found – the third discovered this year. This is almost becoming routine! https://www.space.com/science/astronomy/ uranian_moons.html
————————————
Dr. Anne Kinney, currently with the Space Telescope Science Institute, has been appointed our Science Program Director for the Astronomical Search for Origins & Planetary Systems. I’ll get a bio posted ASAP on our Senior Personnel page at https://spacescience.nasa.gov/ossbios.htm
————————————
Liquid water found in a second meteorite – by the same researcher who announced the first discovery last month. Watch out for this long url: https://www.chron.com/content/interactive/space/astronomy/news/ 1999/solarsys/990907.html
————————————
On Mars, there is a white rock mound covering over 200 square kilometers. According to a team of researchers in Scotland and Turkey, the mound looks like those built by bacteria over 3 billion years ago here on Earth. https://www.newscientist.com/ns/19990904/newsstory12.html
————————————
The near-term shuttle launch schedule (including the launch date of the next Hubble servicing mission) has not yet shaken out. The shuttle folks are still wrestling with wiring problems; obviously, safety is a paramount concern. Story at https://abcnews.go.com/sections/science/DailyNews/shuttle_wiring990903.html
————————————
Cassini Moon images show camera is in top form – Cassini did some useful things while it was slingshotting past earth. Story at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/99/csmoonimagead.html
————————————
Finally, a couple things I haven’t posted yet but bear watching: Mars Climate Orbiter will be arriving at the Red Planet and going into orbit on September 23; you can follow that at https://mpfwww.jpl.nasa.gov/msp98/orbiter/ . And the U.S. House of Representatives is meeting a few blocks away from me right now, debating NASA’s FY 2000 Budget (the scary version passed by the House Appropriations committee). More news on that later.
Cheers!
September 1, 1999
Greetings!
Here’s what’s new at https://spacescience.nasa.gov :
————————————
The best news, in case you hadn’t heard: NASA UNVEILS FIRST IMAGES FROM CHANDRA X-RAY OBSERVATORY – It works! YESSS!!! The first 2 images, of supernova remnant Cass A and a distant quasar, were released last Thursday, and each of them held a surprise. Then, over the weekend Chandra made the most precise measurements ever recorded of the energy output from the 10-million-degree corona of a star. A new era in astronomy has begun.
Chandra home and first images: https://chandra.harvard.edu/index.html
Stellar corona measurement: https://web.mit.edu/newsoffice/nr/1999/chandra.html
————————————
The near-term shuttle launch schedule, including the launch date for the next Hubble servicing mission, may be announced tomorrow. I’ll post it on the Space Science web as soon as we hear from the shuttle folks. You can also follow the shuttle mission story at https://spaceflight.nasa.gov/shuttle/future/sts-103.html
————————————
There was a coronal mass ejection from the Sun over the weekend (not a rare event in itself), carrying perhaps billions of tons of plasma, that was thought to have the potential for generating significant aurorae on Earth, since it was headed close to our vicinity. However, our space weather seems to be little affected as yet. You think it’s hard to forecast hurricanes?
CME story: https://science.nasa.gov/newhome/headlines/ast31aug99_1.htm
space weather page: https://www.sel.noaa.gov/today.html
————————————
On Thursday, September 2 at 10-11 p.m. Eastern time, ABC TV will be showing “Looking for Life” (i.e., in space) as part of an ongoing “Nightline” series. Astrobiology makes the networks! Featuring music from They Might Be Giants, amongst other intriguing elements. ABC promo at https://abcnews.go.com/onair/Nightline/nlpt990729_promo.html#sept2
————————————
The closest pictures ever taken by Galileo of Jupiter’s volcanic moon Io,and several other new images, are now available at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/
————————————
Astronomers have used the world’s two most powerful radar telescopes to make the most detailed images ever obtained for an asteroid in a near-Earth trajectory. This one looks like a spud, too. https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/99/1999jm8.html
————————————
Cracking open a meteorite that fell in West Texas last year, scientists found, much to their surprise, a drop of salty water. https://abcnews.go.com/sections/science/DailyNews/meteorite990826.html
————————————
Pulsars are small spinning neutron stars which send out beams of radio waves. A pulsar has been found that is spinning slower than current theory predicts is possible. I guess nobody ever taught it astrophysics. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/1999/08/990825183711.htm
————————————
A strip of gentle, rolling plains near the Martian South Pole will serve as a welcome mat when our Mars Polar Lander touches down on the Red Planet on December 3. The landing site was unveiled last week. press release, images and more info: https://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msp98/lander/
————————————
Symbiotic Star Blows Bubbles into Space – A tempestuous relationship between an unlikely pair of stars may have created an oddly shaped, gaseous nebula that resembles an hourglass nestled within an hourglass. HST results and pretty images at https://oposite.stsci.edu/pubinfo/pr/1999/32/
Cheers!
August 24, 1999
Just a few new things at https://spacescience.nasa.gov :
————————————
Our Chandra X-ray Observatory has been successfully completing its post-launch checkout, and the first images from the world’s most powerful x-ray telescope will be unveiled at a media briefing at 1 p.m. EDT Thursday, August 26. The images include the spectacular remnants of a supernova and other astronomical objects. The Hubble of X-rays has arrived! The CXO page is at https://chandra.harvard.edu
————————————
Cassini successfully completed a highly accurate pass of Earth on August 17. Those navigators at JPL really know how to fly! Cassini picked up a boost in speed, sending the spacecraft on toward Saturn in 2004. And while Cassini was flying by earth, it was taking scientific measurements in collaboration with another of our spacecraft, Polar, which routinely studies the regions over Earth’s poles.
Flyby story: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/releases/99/csearthflyby.html .
Science story: https://science.nasa.gov/newhome/headlines/ast17aug99_1.htm
Cassini: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/cassini/
Polar: https://www-istp.gsfc.nasa.gov/istp/polar/
————————————
We have selected three very small satellites, called the Nanosat Constellation Trailblazer mission, as the agency’s latest mission in the New Millennium Program. The mission will validate methods of operating several spacecraft as a system, and test eight technologies in the harsh space environment near the boundary of Earth’s protective magnetic field, or magnetosphere. The New Millennium program has already given us DS1, which has successfully tested ion propulsion and other technologies, and DS2, which will be slamming into Mars in December.
press release: ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/1999/99-095.txt
New Millennium: https://nmp.jpl.nasa.gov/
————————————
Links to the Wide Field Camera 3, a future Hubble Space Telescope science instrument to be installed in 2003 on Servicing Mission 4, have been added to our Missions in Development page. WFC3 is at https://wfc3.gsfc.nasa.gov/
Cheers!
Plasma, Plasma, Everywhere
A new model of the plasmasphere surrounding our world
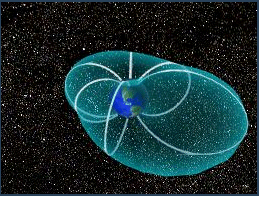
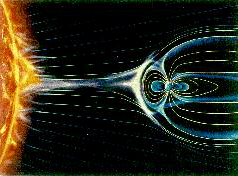
Sept. 7, 1999: As photographed from space, the Earth looks like it is floating in a black void. But, unseen by our eyes and most cameras, the Earth is actually surrounded by a complex system of interacting electric and magnetic fields, electric currents and charged particles called the magnetosphere.
Right: If a camera didn’t compensate for the bright sunlight in space, stars would be seen in the background and the Earth would appear as a bright white orb. Because distant stars aren’t as bright as the Earth, a low photo exposure results in a black background.
The magnetosphere provides a barrier between our planet and particles continually given off by the Sun’s corona called the “solar wind.” These particles constitute a plasma – a mixture of electrons (negatively charged) and ions (atoms that have lost electrons, resulting in a positive electric charge).
Plasma is not a gas, liquid, or solid – it is the fourth state of matter. Plasma often behaves like a gas, except that it conducts electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. On an astronomical scale, plasma is common. The Sun is composed of plasma, fire is plasma, fluorescent and neon lights contain plasma.
“99.9 percent of the Universe is made up of plasma,” says Dr. Dennis Gallagher, a plasma physicist at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center. “Very little material in space is made of rock like the Earth.”
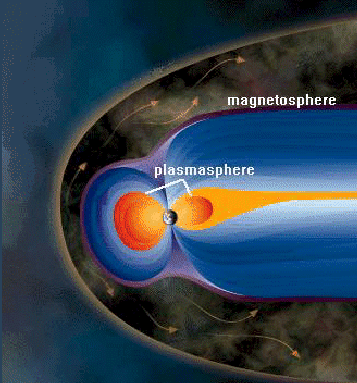
The plasma of the magnetosphere has many different levels of temperature and concentration. The coldest magnetospheric plasma is most often found in the plasmasphere, a donut-shaped region surrounding the Earth’s middle. But plasma from the plasmasphere can be detected throughout the magnetosphere because it gets blown around by electric and magnetic forces.
Above: Artist’s concept of the magnetosphere. The rounded, bullet-like shape represents the bow shock as the magneto- sphere confronts solar winds. The area represented in gray, between the magnetosphere and the bow shock, is called the magnetopause. The Earth’s magnetosphere extends about 10 Earth radii toward the Sun and perhaps similar distances outward on the flanks The magnetotail is thought to extend as far as 1,000 Earth radii away from the Sun.
Gallagher has developed a general model to describe the density of the plasma surrounding the Earth. His paper, “Global Core Plasma Model,” will be published in the Journal of Geophysical Research. “Core plasma” refers to the low-energy plasma (zero to 100 electron volts) that makes up the plasmasphere. The plasmasphere extends out to as little as 2 to 3 Earth radii and, under quiet conditions on the evening side, perhaps more than 6 Earth radii.(Because conditions in space constantly vary and regions never have exact boundaries, plasma physicists measure the plasmasphere relative to the size of Earth: 4,000 miles [6,400 km] is about one Earth radius.) The extent of the plasmasphere depends on space weather activity. High levels of activity erode the plasmasphere; long periods of quiet allow the plasmasphere to expand.
Rockets, satellites and the space shuttle have flown in parts of the core plasma neighborhood. By taking various measurements of this region, scientists have gradually come to understand the basic nature of the entire plasmasphere.
“We’ve been flying in plasma for over 40 years and have slowly gained a statistical picture of what things are like, such as the density and proportion of oxygen, hydrogen, and helium,” says Gallagher.
But our understanding of the plasmasphere is not complete. For one thing, all the various measurements have resulted in many independent models of specific plasma regions. By combining previous work, Gallagher’s model attempts to describe, mathematically, a general, complete image of the plasmasphere.
“This model begins to paint a picture, but it’s something of a Frankenstein’s monster,” says Gallagher, referring to how his model is pieced together from several different, dissimilar models. “A significant issue is how you smooth the stitches.”
Gallagher’s model combines the International Reference Ionosphere (IRI) model for low altitudes with higher altitude models. The part of our atmosphere that contains plasma – the ionosphere – is generally 90 to 1,000 km (54-620 mi.) above the ground.
The shorter wavelengths of sunlight, ranging from the ultraviolet to X-rays, ionize the Earth’s upper atmosphere by tearing electrons off atoms. The ions and electrons do not readily recombine in the ionosphere because particle collisions are infrequent in the rarified atmosphere. Ionospheric densities range from a peak of about 1 million particles/cm3 down to many thousands of particles/cm3. The densities continue to fall as you move to higher altitudes.
From the equator to the middle latitudes of Earth, the ionosphere joins smoothly with the plasmasphere. Beyond the outer boundary of the plasmasphere, the densities of plasma in the magnetosphere can fall as low as 0.01 particles/cm3.
“The plasma environment around the Earth is a natural extension of Earth’s atmosphere, ionized by the Sun,” says Gallagher. “Any planet that has an atmosphere is going to have energy from the Sun imparted to the atoms. The consequences are that lighter elements escape. But Earth’s magnetic field traps much of this escaping gas. A planet like Mars that has, at best, a weak magnetic field, also has a very thin atmosphere. Some researchers have speculated that the Earth’s magnetic field may play a role in slowing the loss of our atmosphere into space.”
Our atmosphere provides pressure, proper temperature, and oxygen – fundamental requirements for life on Earth. Without the atmosphere, one side of our planet would freeze while the other would broil under intense solar radiation.
Gallagher’s model may contribute to our understanding of how the Earth’s plasma affects our quality of life. Radio waves and power lines are affected by the presence of plasma, as are satellites and the Space Shuttle. Plasma can cause an electric charge to accumulate on one part of a spacecraft but not another, sometimes resulting in an electric arc, or discharge. These electric arcs can disrupt or destroy sensitive electronic components.
Gallagher will be able to refine his model with data from the IMAGE satellite, due to launch in February 2000. IMAGE will give us a better picture of the Earth’s magnetosphere, and because plasma is bound to magnetic fields, IMAGE should also improve our understanding of how the plasmasphere and the magnetosphere interact.